Matcha Effect: How does Matcha tea affect the body?

Matcha Effect: How does Matcha tea affect the body?
When brewed with hot water, the green powder is pure enjoyment. If you're new to matcha tea , you should definitely give it a try. Besides its delicious taste, this superfood also offers numerous benefits.
In this blog post, we will show you exactly how matcha works in your body and what you should pay attention to when consuming it.
Matcha: cultivation and production
In order to be fully informed about the benefits and effects of matcha on your body, it is first important that you know how matcha is grown and produced.
The Japanese word matcha simply means "ground tea." It was in Japan that the production of this tea specialty was perfected—even though the tea originally comes from China.
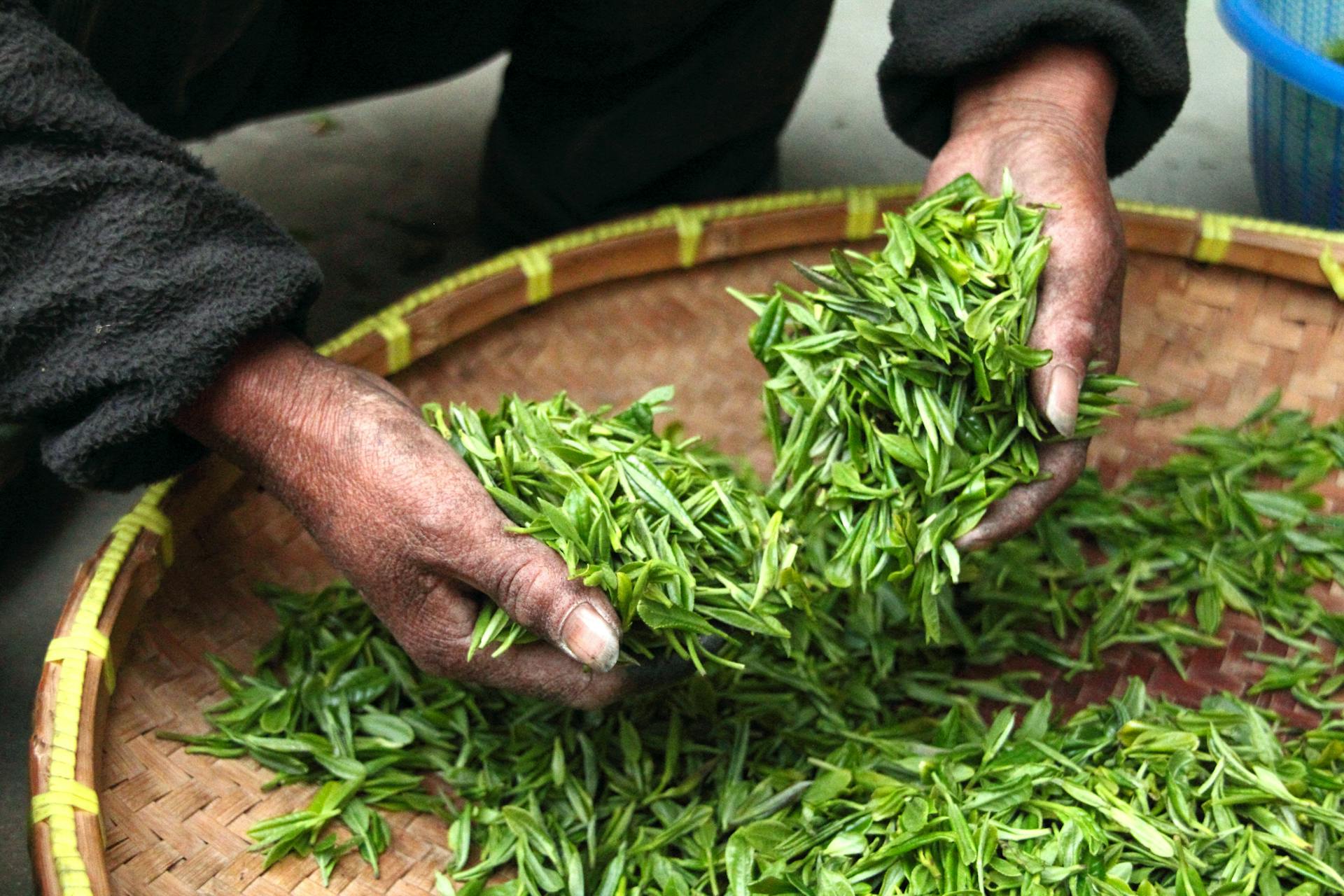
Matcha tea cultivation is characterized by shading the tea plants for approximately three to four weeks before harvest, allowing the tea leaves to ripen in the shade. Only 90% of the light penetrates the nets covering the plants. This stimulates the production of chlorophyll, which extends the ripening time.
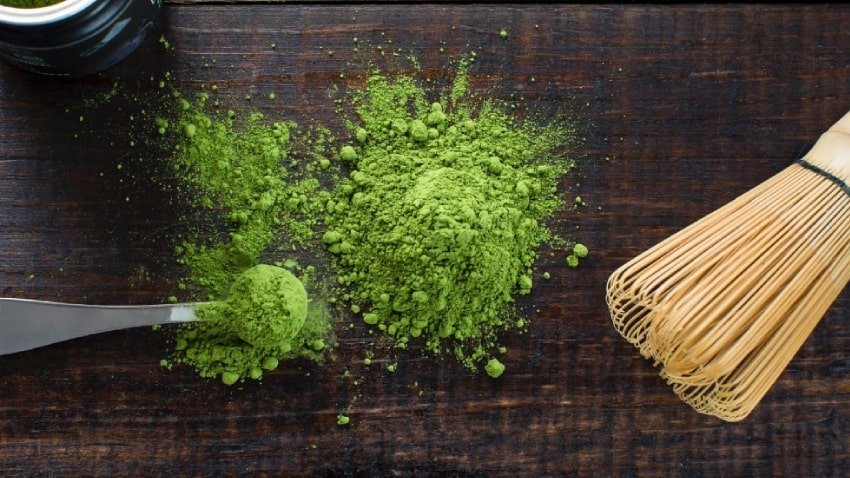
After the tea leaves are harvested, they are first steamed and then dried. To produce this high-quality tea, the leaf tissue is separated from the stems and the fine leaf veins using an air-blast process. The leaf tissue is then ground on granite stone mills, which ensures the powder's vibrant green color. It takes approximately one hour to produce 30 grams of this fine powder.
Nutrients contained in Matcha
The entire manufacturing process of the high-quality Matcha tea powder is important not only to ensure that the light green color shines so beautifully, but also to ensure that the valuable nutrients of the tea are not lost.
Ground green tea contains numerous nutrients, such as vitamins, minerals, calcium, and potassium. Matcha also contains a high concentration of beta-carotene, which is important for the eyes, skin, and metabolism, as it is a precursor to vitamin A. Secondary plant compounds, in this case the antioxidants contained in matcha, also have health-promoting effects. Matcha, for example, has an even higher ORAC value—which indicates the antioxidant capacity of a food—than the valuable acai berries.
In addition to important nutrients, matcha also contains caffeine, or theine—and a lot of it. Depending on how much of the green powder you use in your tea or smoothie, the drink or dish can even be comparable to an espresso in terms of caffeine concentration.
Health effects of matcha in your body
After all this information, you're probably wondering what actually happens when you consume matcha, or more specifically, what happens in your body and how it reacts to matcha.
The thing you'll actually "feel" most about matcha is the gentle energy boost you get from the caffeine in the tea. It's said to be a gentle boost because the caffeine is in a bound form, thus gradually developing its invigorating effect. With coffee, the boost is almost instant and all at once. In matcha tea, the caffeine is absorbed more slowly by the body and also takes effect over a longer period of time.
In addition to the gentle caffeine kick, the caffeine in matcha also promotes concentration and stimulates the circulation – a definite benefit of matcha.
Drinking Matcha during pregnancy
Because high-quality matcha tea and powder also contain caffeine, pregnant women should consume it in moderation. Pregnant women should not consume more than 200 to 300 milligrams of caffeine per day. Even in one cup of matcha tea, this limit can quickly be reached and even exceeded. Be sure to consult your doctor if you want to enjoy our green matcha tea during pregnancy.
Matcha tea effect in the evening: good or bad?
The caffeine in matcha will have a different effect on each person. If you have trouble falling asleep, you shouldn't drink matcha tea before bedtime. Since you don't know exactly how much caffeine is actually contained in a cup of tea, you should avoid it altogether. Of course, you can always do the self-test and drink a small cup of tea three to four hours before bedtime. It's believed that caffeine stays in the body for up to eight hours, so if you have a 10:00 p.m. bedtime routine, you shouldn't drink matcha after about 2:00 p.m.
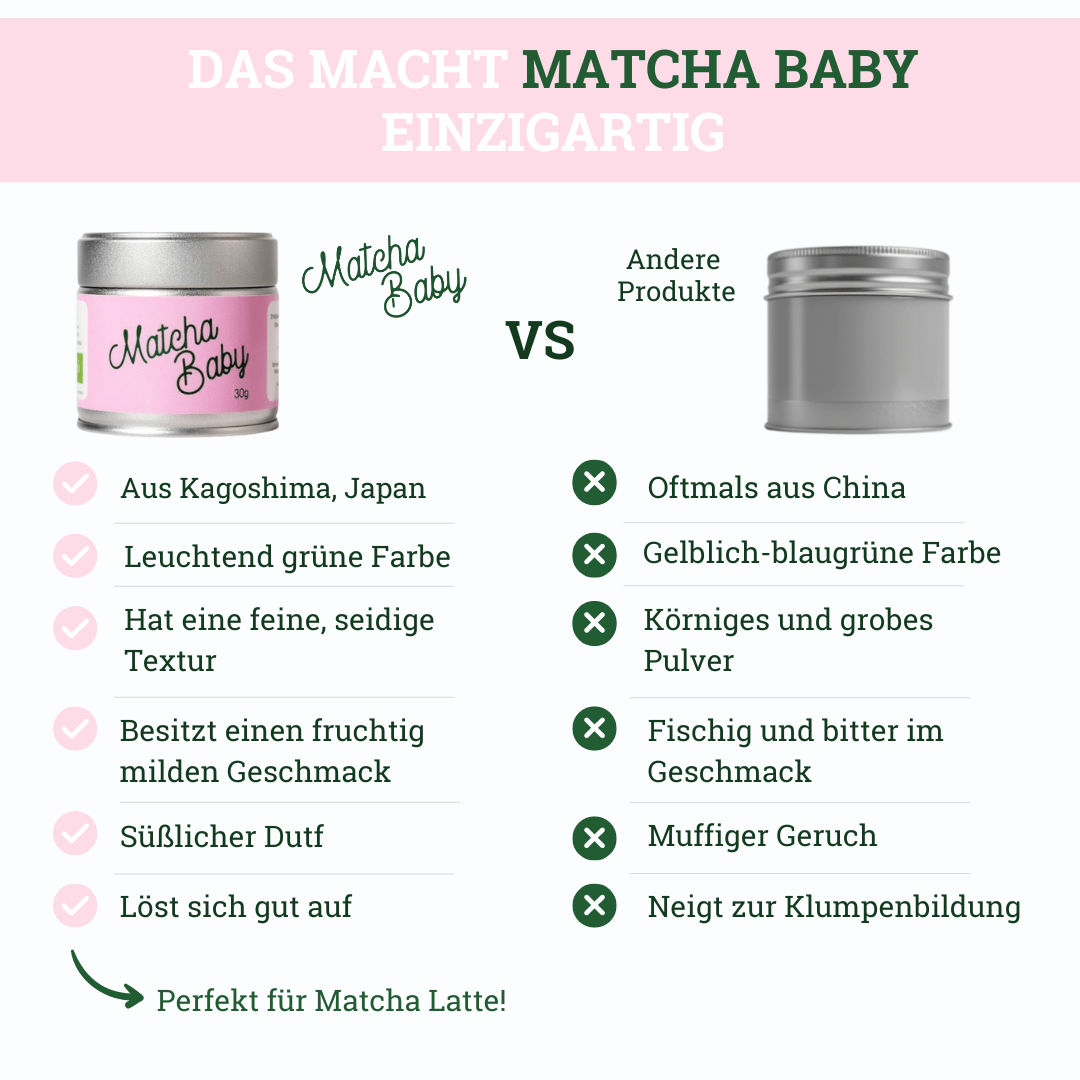
Fine powder? Pay attention to the quality of your matcha!
Regardless of whether you're drinking matcha to help you focus at work or need a gentle caffeine kick to keep you awake after your lunch break, always make sure your matcha powder is of good quality. You can recognize high-quality matcha tea by its bright green color. Matcha tastes slightly sweet and not overly bitter. You can recognize inferior quality by its slightly yellowish or brownish color. Inferior tea also tastes a bit too bitter.
Matcha Effects FAQs
Since we know that there are numerous questions about the enjoyment and effects of matcha powder, we have briefly answered four frequently asked questions in this FAQ section.
Is matcha healthy every day?
Matcha tea is healthy and can be safely consumed every day. If matcha is a regular part of your daily routine, however, make sure you don't drink more than 1 to 2 cups of matcha tea per day.
Can you sleep after drinking matcha?
Whether you can sleep after drinking matcha depends entirely on the individual. Every organism reacts and processes the caffeine in matcha differently, so it's impossible to make a general statement.
What should you pay attention to with Matcha?
When it comes to matcha, you need to make sure you buy high-quality powder and not consume too much per day. Good matcha powder can be recognized by its bright green color and slightly sweet taste.
When should you not drink matcha?
You should not drink matcha if you are taking certain medications. Pregnant and breastfeeding women, as well as children, should also avoid consuming too much or even no matcha at all.
Conclusion: Positive effect
High-quality matcha certainly has a positive effect on the body, but it should still be consumed in moderation. Of course, we'd love to only drink matcha lattes, matcha tea, and matcha smoothies, but then that wouldn't be anything special. If you eat ice cream every day, you'll quickly get fed up after the first few weeks, right?!
If you drink matcha occasionally and mix a few grams of matcha into savory dishes or desserts, you'll reap the numerous benefits of matcha powder. However, be careful if you're taking certain medications, are pregnant or breastfeeding, or if you're making tea or other dishes for children. The high caffeine content in matcha powder does increase alertness, but it can be intolerant to some people. Always ask your doctor if it's safe to consume this green beverage.